- [MySQL] 19. 시나리오 코드로 관계 차수 이해하기 : 야구 팀과 야구 선수2024년 06월 04일
- Song hyun
- 작성자
- 2024.06.04.:38
728x90반응형[MySQL] 19. 시나리오 코드로 관계 차수 이해하기
* 참고하면 좋은 글: https://whatsthatsound.tistory.com/243
[MySQL] 18. 관계 차수
[MySQL] 18. 관계 차수1. 관계 차수란?2. 테이블 차수와 관계 차수 3. 테이블 간의 관계 정의 1. 관계 차수란? 2. 테이블 차수와 관계 차수 3. 테이블 간의 관계 정의 (1) 1:1 관계(2) 1:N 관계(3) N:1 관계
whatsthatsound.tistory.com
예제 코드를 통해 관계 차수의 개념을 이해해보자.
1. 생각해보기: 야구 팀-야구 선수 테이블 만들기

누가 기준이 되어야 할까? -표를 그려서 시각화해보자: 한 팀은 여러 명의 선수를 지닐 수 있다. 하지만 한 선수는 한 팀에만 속할 수 있다.
한 팀은 여러 명의 선수를 지닐 수 있다.(팀:선수) => 1:N
한 선수는 한 팀에만 속할 수 있다.(선수:팀) => N:1
-관계의 방향성을 명확히 하자.
(1) TB_Team
create table TB_Team( team_id int auto_increment primary key, team_name varchar(50), home_city varchar(50), esteblished_year year );(2) baseball_team
create table TB_Player( player_id int auto_increment primary key, player_name varchar(50), position varchar(20), birth_date date, team_id int, foreign key(team_id) references TB_Team(team_name) );*예시
더보기create table TB_User( user_id int auto_increment, username varchar(50) not null, password varchar(50) not null, primary key(user_id) ); create table TB_User_Details( details_id int auto_increment, user_id int unique, address varchar(100), phone_number varchar(15), email varchar(50), primary key(details_id), foreign key(user_id) references tb_user(user_id) );
2. 생각해보기: 학생-수업 테이블 만들기
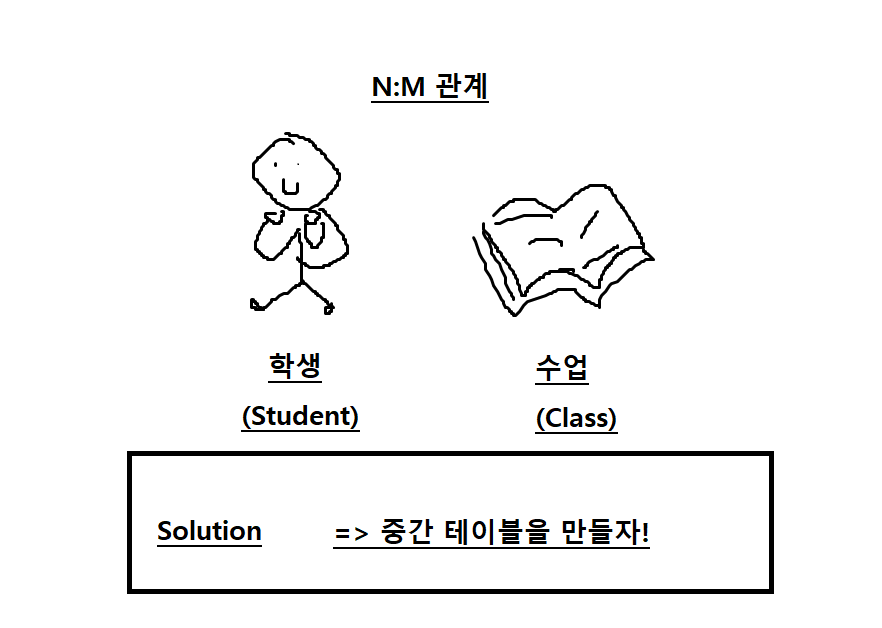
- 한 학생이 여러 수업을 들을 수 있다. (학생:수업 = N:M)
- 한 수업에 여러 학생이 들으러 올 수 있다. (수업:학생 = N:M)
=> 학생-수업을 이어주는 중간 테이블(=수강 정보 테이블)을 만들자!
(1) 학생, 수업, 수강 정보 테이블 만들기
create table TB_Student( student_id int auto_increment primary key, student_name varchar(100) not null ); create table TB_Class( class_id int auto_increment, class_name varchar(100), teacher varchar(100) not null, primary key(class_id) ); -- 학생과 수업 테이블은 N:M 관계가 된다. -- 중간 테이블 설계 (수강 등록 테이블) create table TB_Registration( student_id int, class_id int, registration_date date, foreign key(student_id) references TB_Student(student_id), foreign key(class_id) references TB_Class(Class_id) );(2) 복합키 만들기
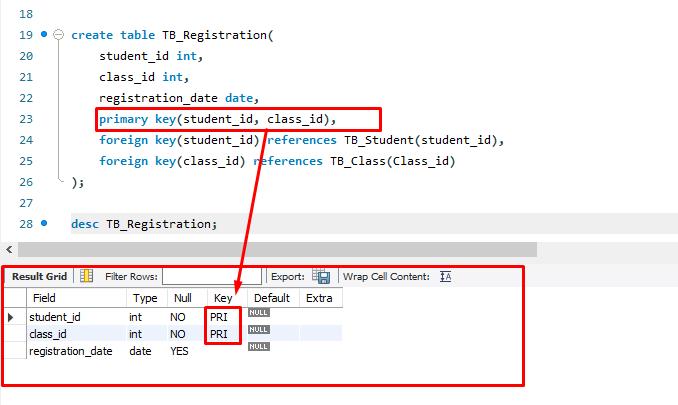
primary key(student_id, class_id)(3) 데이터 입력하기
create database mydb2; use mydb2; create table TB_Student( student_id int auto_increment primary key, student_name varchar(100) not null ); insert into TB_Student values (1,'홍길동'), (2,'전우치'); create table TB_Class( class_id int auto_increment, class_name varchar(100), teacher varchar(100) not null, primary key(class_id) ); insert into TB_Class values (1,'수학','신사임당'), (2,'국어','세종대왕'); -- 학생과 수업 테이블은 N:M 관계가 된다. -- 중간 테이블 설계 (수강 등록 테이블) create table TB_Registration( student_id int, class_id int, registration_date date, primary key(student_id, class_id), foreign key(student_id) references TB_Student(student_id), foreign key(class_id) references TB_Class(Class_id) ); insert into TB_Registration values (1,2,'2024-01-01'), (2,1,'2024-06-06'); desc TB_Registration; select*from TB_Student; select*from TB_Registration;728x90반응형'MySQL > 기본 개념 및 지식' 카테고리의 다른 글
[MySQL] 21. OUTER JOIN (0) 2024.06.05 [MySQL] 20. JOIN (0) 2024.06.05 [MySQL] 18. 관계 차수 (0) 2024.06.04 [MySQL] 17. 도전 문제: 테이블 및 문제 만들기 (0) 2024.06.04 [MySQL] 16. INDEX 인덱스 (0) 2024.06.04 다음글이전글이전 글이 없습니다.댓글
스킨 업데이트 안내
현재 이용하고 계신 스킨의 버전보다 더 높은 최신 버전이 감지 되었습니다. 최신버전 스킨 파일을 다운로드 받을 수 있는 페이지로 이동하시겠습니까?
("아니오" 를 선택할 시 30일 동안 최신 버전이 감지되어도 모달 창이 표시되지 않습니다.)