728x90
반응형
[자료 구조] 3. Java 배열을 활용한 객체 만들기
1. 배열에 대한 기본 개념
2. 배열을 활용한 객체를 만들어보자.
1. 배열에 대한 기본 개념
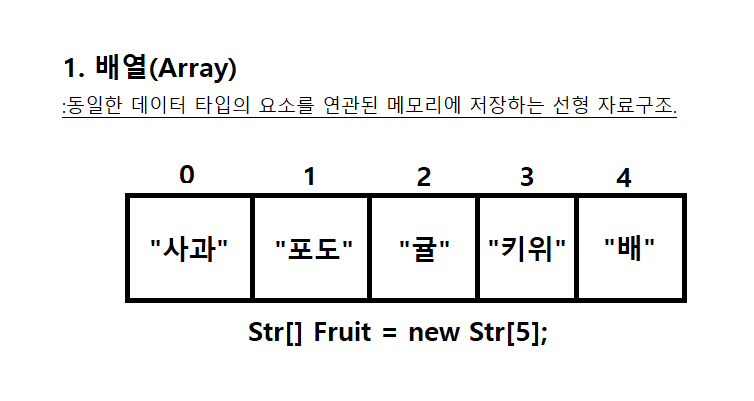
(1) 배열의 개념: 동일한 데이터 타입을 순서에 따라 관리하는 자료 구조
(2) 배열의 특징:
-정해진 크기가 있다. (배열)
-요소의 추가와 제거시, 다른 요소들의 이동이 필요하다.
-배열의 i번째 요소를 찾는 인덱스 연산이 빠르다.
-jdk 클래스: ArrayList, Vector
2. 배열을 활용한 객체를 만들어보자.
package Structure;
/*
* 배열을 활용한 클래스를 설계해보자.
* 물론, 이미 자바 표준 API 개발자들이
* 잘 만들어 준 클래스들이 존재한다.
* 하지만 직접 기능을 확장해서 만들어 보자.
*/
public class TencoIntArray {
int[] intArr;
int count; // 배열 안에 들어간 요소의 갯수
public final int ARRAY_SIZE;
public static final int ERROR_NUM = -99999;
public TencoIntArray() {
count = 0;
ARRAY_SIZE = 10;
intArr = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
}
public TencoIntArray(int size) {
count = 0;
ARRAY_SIZE = size;
intArr = new int[ARRAY_SIZE];
}
// 기능 설계
// 배열 요소의 제일 뒤의 값을 추가하는 기능을 가진다.
public void addElement(int inputData) {
// 방어적 코드 필요
if (count >= ARRAY_SIZE) {
System.out.println("메모리 공간이 가득 찼습니다.");
return; // 실행의 제어권 반납
}
intArr[count] = inputData;
count++;
}
// 배열에 요소를 추가하는 기능
// 배열에 지정된 인덱스 위치의 값을 추가하는 기능
public void insertElement(int position, int inputData) {
// 방어적 코드 작성 1
if (count >= ARRAY_SIZE) {
System.out.println("메모리 공간이 가득 찼습니다.");
return;
}
// 방어적 코드 2
// 10 0
if (position < 0 || position > ARRAY_SIZE) {
System.out.println("지정한 인덱스 번호가 잘못 되었습니다.");
return;
}
// 요청 값: position -> 3
// 현재 [11,12,13,14,15]
for (int i = (count - 1); i >= position; i--) {
intArr[i + 1] = intArr[i]; // 하나씩
// intArr[5] = 15; 수행1
// intArr[4] = 14; 수행2
}
intArr[position]=inputData;
count++;
}
// 지정한 인덱스 번호에 요소를 꺼내주기
public int getElements(int position) {
if(position<0 || position>(count-1)) {
System.out.println("검색 위치 오류. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count+ "개 입니다.");
return ERROR_NUM;
}
return intArr[position];
}
// 요소를 전체 출력하는 기능 만들어 주기
public void printAll() {
if(count==0) {
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없습니다.");
return;
}
//
//for (int i : intArr) {
for(int i=0; i<intArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(intArr[i]);
}
}
// 전체 삭제 기능
public void removeAll() {
for(int i=0; i<intArr.length; i++) {
intArr[i]=0;
}
// 요소의 갯수 상태를 항상 관리하고 처리해야 한다.
count++;
}
// 배열의 크기가 아닌 현재 요소의 갯수를 반환하는 것
public int getCountSize() {
return count;
}
// 현재 요소가 하나도 없는 상태이다.
public boolean isEmpty(){
if(count==0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 지정한 인덱스 번호에 요소를 삭제하는 기능
public void removeElement(int position) {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("삭제할 요소가 없습니다.");
}
// 인덱스 범위를 잘못 지정했다면 방어적 코드
if((position<0) || (position>=count)) {
System.out.println("잘못된 요청입니다.");
}
//intArr[position]=null; -> 사용자가 요청한 인덱스는 0
//[100] [200] [300] [400]
//[200] [300] [400] [0]
// 1 5-1 =4
for(int i=position; i<count-1; i++) {
// 1 2
intArr[i]=intArr[i+1];
}
// 3
count--;
}
// 지정한 인덱스 번호에 맞는 요소를 출력하는 기능
}package Structure;
public class MainTest1 {
// 메인 쓰레드(함수의 시작)
public static void main(String[] args) {
TencoIntArray tencoIntArray = new TencoIntArray();
tencoIntArray.addElement(100);
tencoIntArray.addElement(200);
tencoIntArray.addElement(300);
tencoIntArray.addElement(400);
//tencoIntArray.insertElement(5, 50); // 테스트 이후에 리팩토링 수정 - todo
//tencoIntArray.printAll();
System.out.println("---------------------");
//System.out.println(tencoIntArray.getCountSize());
System.out.println("---------------------");
//System.out.println(tencoIntArray.isEmpty());
System.out.println("---------------------");
//tencoIntArray.removeAll();
//tencoIntArray.printAll();
tencoIntArray.removeElement(2);
tencoIntArray.printAll();
} // end of main
} // end of class728x90
반응형
'자료 구조 > 기본 개념' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료 구조] 6. 큐 구현하기 (0) | 2024.05.07 |
|---|---|
| [자료 구조] 5. 비선형 자료 구조 (0) | 2024.05.03 |
| [자료 구조] 4. 배열을 활용해 Stack 구현하기 (0) | 2024.05.03 |
| [자료 구조] 2. 선형 자료 구조 (0) | 2024.05.02 |
| [자료 구조] 1. 자료 구조 개론: 자료 구조란? (0) | 2024.05.02 |

